How We Love: 7 Types of Romantic Relationships

Have you ever thought about what love is? What do we mean when we say “I love you”?
Poets, philosophers, and psychologists have been offering their explanations of this feeling for many centuries. If you look deeper into their theories, you can find many curious suggestions ranging from “butterflies in the stomach” and “stars in the eyes” to the triangular theory of love by Robert Sternberg. The latter sounds complicated, right?
Let’s see how he explains love and what types of romantic relationships he describes.
 Sternberg’s theory of love presupposes that each component has its evolution time. On the one hand, intimacy always grows as the relationship develops. On the other hand, passion is very intense in the beginning but usually decreases as a relationship develops and even disappears. And finally, a commitment that grows more slowly than intimacy and stabilizes as the relationship strengthens.
Now, let’s consider all kinds of love in detail.
Sternberg’s theory of love presupposes that each component has its evolution time. On the one hand, intimacy always grows as the relationship develops. On the other hand, passion is very intense in the beginning but usually decreases as a relationship develops and even disappears. And finally, a commitment that grows more slowly than intimacy and stabilizes as the relationship strengthens.
Now, let’s consider all kinds of love in detail.
 This is what the triangular theory of love of R. Sternberg says. We hope with the help of it, you will identify what type of relationship you have and what you should be thinking and working on. But remember, love is beautiful in any case.
This is what the triangular theory of love of R. Sternberg says. We hope with the help of it, you will identify what type of relationship you have and what you should be thinking and working on. But remember, love is beautiful in any case.
Contents
hide
The triangular theory of love by Robert Sternberg
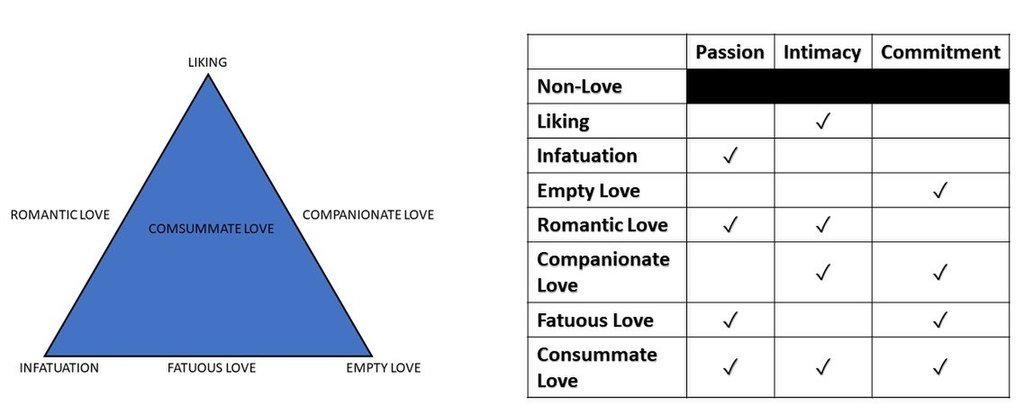
According to his triangular theory of love developed by a famous psychologist from Yale University, R.Sternberg, there are seven kinds of love based on relationship types. The professor describes how different kinds of interpersonal relationships may combine and create several kinds of love. Robert says that all human relationships consist of three main components: commitment, passion, and intimacy.- Commitment – In the short-term, the decision that “I love her” or “I love him”, and in the long-term, one’s commitment to maintain that love.
- Passion – The feelings that lead to romance, physical attraction, sexual consummation.
- Intimacy – The feelings of closeness, connectedness, and bondedness in loving relationships.
 Sternberg’s theory of love presupposes that each component has its evolution time. On the one hand, intimacy always grows as the relationship develops. On the other hand, passion is very intense in the beginning but usually decreases as a relationship develops and even disappears. And finally, a commitment that grows more slowly than intimacy and stabilizes as the relationship strengthens.
Now, let’s consider all kinds of love in detail.
Sternberg’s theory of love presupposes that each component has its evolution time. On the one hand, intimacy always grows as the relationship develops. On the other hand, passion is very intense in the beginning but usually decreases as a relationship develops and even disappears. And finally, a commitment that grows more slowly than intimacy and stabilizes as the relationship strengthens.
Now, let’s consider all kinds of love in detail.
7 types of love
Sternberg identified 7 types of love depending on the different types of relationships people have.#1. Infatuation (Passion)
You know how it feels: our heart is beating madly, eyes are glowing, and we can’t think about anything except our object of love, which’s why it’s called infatuation. When we are talking about love at first sight with a beautiful stranger, it’s passion. There is no intimacy or commitment here, but passion makes our life bright and full of emotions.#2. Liking (Intimacy)
Intimacy can be a platonic feeling, and this feature differs intimacy from passion. We feel intimacy with our close friends: we like their way of life, their behavior, personality, we can speak about everything with them, we feel safe and convenient with them. Intimacy can turn into something bigger and be a basis for love with passion and commitment.#3. Empty love (Commitment)
When passion and intimacy have gone from the long-term relationship, it’s time for commitment, the end of romantic love. But we still continue to take care of the partner.#4. Fatuous love (Commitment and Passion)
It’s an interesting kind of romantic relationship that leads to spontaneous Vegas weddings. People feel the passion and want to turn it into something bigger. Into a marriage, for example. The issue is they don’t know the personalities of each other. It leads to loud fights and showdowns when the opinions of partners differ. If passion passes away or becomes annoying, such romantic relationships end with divorce.#5. Romantic love (Passion and Intimacy)
This love is what we see in all romantic novels. You like the personalities of each other, want to share ideas, talk till the morning, and feel physical attraction. Partners in such a relationship don’t want or aren’t ready to commit to each other. For example, they can live in different cities and have a good time on vacations, none of them wants to move and change their lives. This kind of love is focused on the present moment, not the future. When partners are ready to add the commitment into relationships, it can lead to perfect love.#6. Companionate love (Intimacy and Commitment)
Companionate love is opposed to romantic love. It is a deep emotional connection and means more than just friendship. This is close and convenient relations without passion and physical attraction, something that can happen after several years of meeting between friends, like agreement. It means the growth of relationships and gives a chance for a healthy and beautiful feeling.#7. Consummate love (Intimacy, Commitment, and Passion)
It’s a perfect kind of love that includes all important components in equal proportions. If you are still happy with your partner several years after your first date, enjoy time together, take care of each other, and your nights are full of passion, this is consummate love.Sternberg’s love triangle summary

Triangular Theory of Love (Sternberg, 1988)

Leave a Reply